- JTEKT TOP
- Sustainability
- Environmental Report
- Establishment of Recycling Society
Establishment of Recycling Society
Preservation of the world's resource bases is a major theme of ISO26000, GRI Standards 2016, and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). There is also a strong demand on companies to reduce their usage of raw materials and to utilize recycled parts. In addition, due to the concern of global water shortages in the future, it is becoming increasingly important for companies to engage in activities for the effective utilization of water resources. At JTEKT, through promotion of production technology innovations, reduction of production processes and subsequent reduction of materials, and improvements and ingenuity at the production site, we are proceeding with various initiatives to reduce waste and reuse and recycle resources including water.
Main FY2022 Results
Environmental Action Plan 2025/FY2022 Activity Result
[ ] vs FY2018
| Category | Initiative items | Targets and Initiatives | FY2022 Activity Result | Evaluation | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effective use of resources | 《Production》 (1) Promotion of thorough reduction of emissions through source control (2) Reduction of final disposal volume through recycling |
《Production》 ①Source control such as changes in net shape, design, construction method, etc. ② Ongoing efforts to maintain zero landfill waste
|
|
◯ | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (3) Reduction of water consumption in production | ① Promote reuse, save water and reduce waste ② Strengthen water reduction and improve water management level at high-risk sites based on water risk assessment
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 《Logistics》 Reduction of one-way packaging material usage |
① Reduce the use of packaging materials by simplifying packaging and increasing the number of returnable containers.
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (2) Reduction of the amount of disposable plastics used and adoption of bioplastics 3R promotion (Reduce/Reuse/Recycle), confirmation of market trends of bioplastics
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Activity Report
Waste Reduction <Production>
Initiatives for waste generated in large quantities
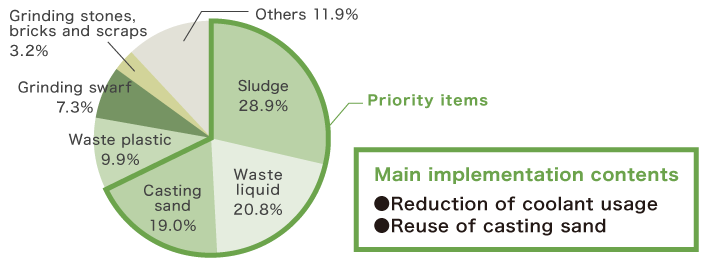
JTEKT engages in efforts to categorize waste materials (recycling items for free or at a charge) and prioritizing improvements for waste for which there are high discharge volumes with a focus on the major items of sludge, casting sand, and waste oil, designating as priority items.
Percentage of waste in FY2022 (JTEKT alone)
Initiatives to achieve zero emissions
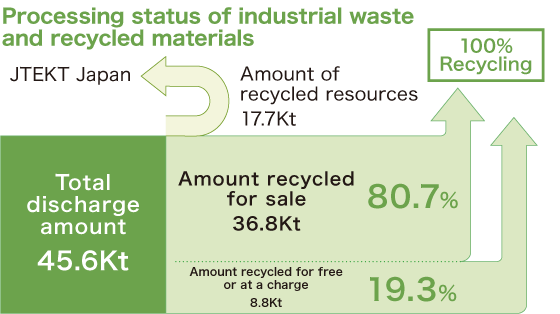
JTEKT considers all discharged materials, including waste, to be resources, and we have been working to achieve a 100% recycling rate based on the concept of 3R (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle).
JTEKT alone achieved the 100% recycling rate in November 2012, which we have maintained ever since. We will formulate and promote plans for each region in order to achieve zero emissions on a company-wide basis.
What is "Zero Emission"?
The practice of utilizing waste and byproduct created through industrial activities as resources for other industries in an attempt to avoid releasing waste into the natural world on the whole. This concept was proposed by the United Nations University in 1994.
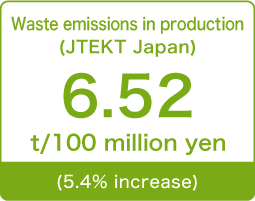
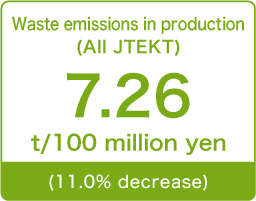
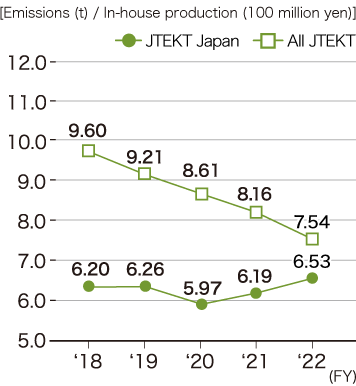
Transition in discharge amount
JTEKT Japan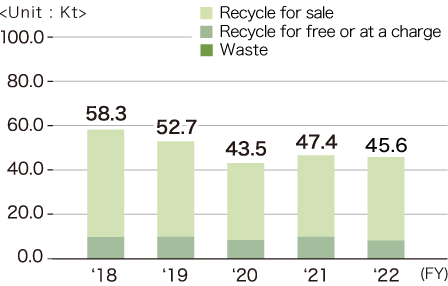
All JTEKT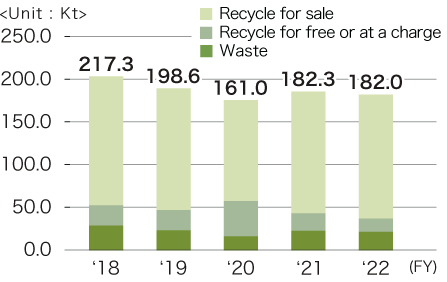
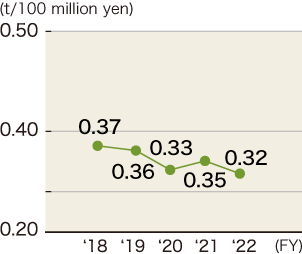
Transition of waste basic unit
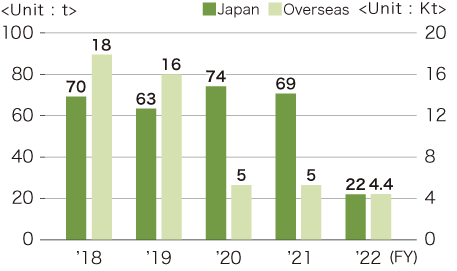
Transition of hazardous waste emissions
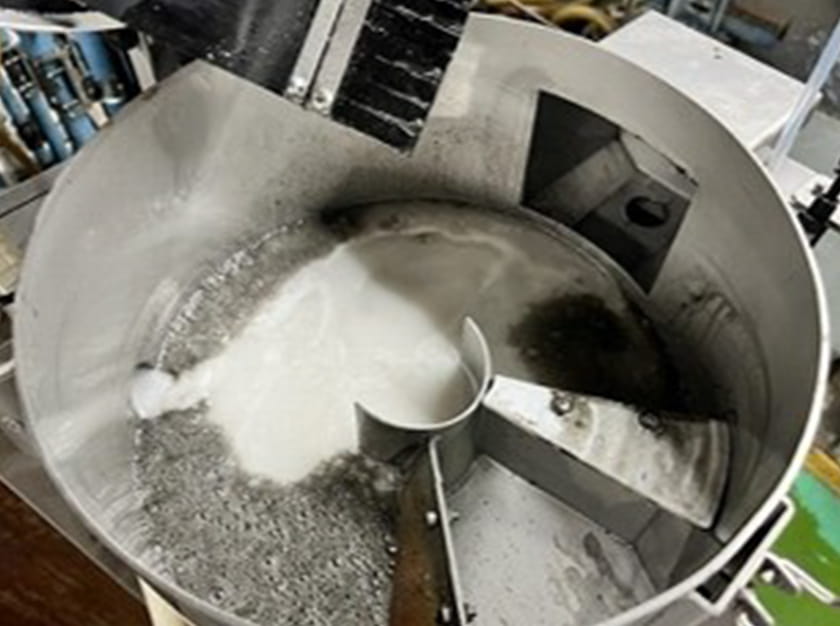
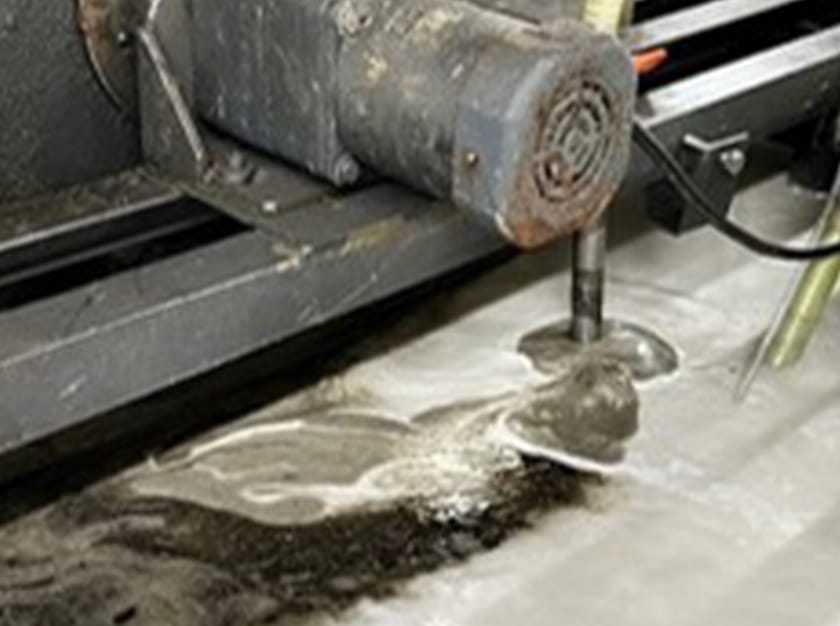
Main implementation contents
Hamura Plant
Longer life of pre-quenching cleaning solution due to floating separation effect of microbubbles
In the pre-heat treatment cleaning process at Hamura Plant, the amount of sludge brought in from the previous process was large and the cleaning solution deteriorated quickly, so we had to change the solution every day and used about 37,000m³ of water and 4m³ of cleaning solution per year.Therefore, aiming to extend the life of the solution, we have introduced a floating separation equipment using microbubbles to remove sludge from the cleaning solution.The installation of the equipment removed the sludge in the cleaning solution and reduced the frequency of changing the cleaning solution to once per three days.This resulted in a reduction in water consumption of approximately 24,000m³ per year and the clearning solution consumption of approximately 3m³.

Removing fine sludge

Oil recovering
Waste reduction<Logistics>
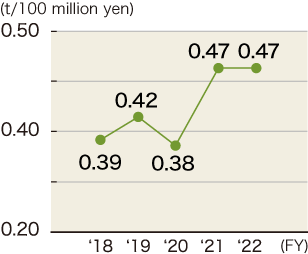
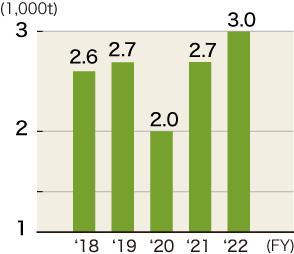
Reduction of packaging materials
In order to promote reduction of wooden packaging materials, we expanded the change from wooden pallets to resin pallets, and from wooden boxes to reinforced cardboard boxes. Also, In order to promote reduction of paper packaging material, we expanded the change from disposable carboard boxes to returnable polyethylene cases. We reviewed excess packaging and changed to the use of cardboard boxes matching with product sizes in an effort to reduce the amount of cushioning material.
As a target for FY2023, JTEKT strives to achieve a wooden packaging material basic unit of 0.31t/100 million yen and paper packaging material basic unit of 0.41t/100 million yen.
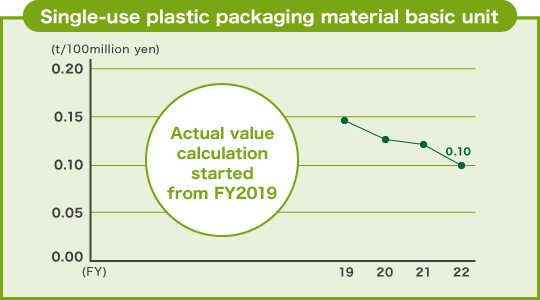
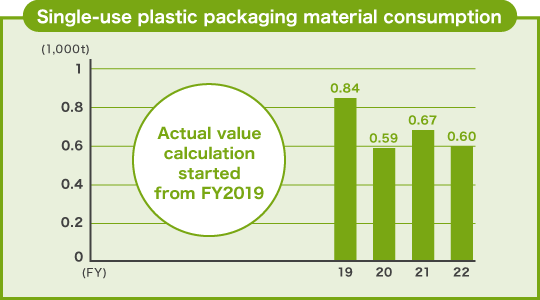
Reduction of single-use plastic packaging material
JTEKT started tracking disposable plastic packaging material as part of our SDGs initiatives in FY2021. Our reduction efforts included a use of vacuum packaging for leather-wrapped large-size bearings and an expansion of the use of belt lashing.
As a target for FY2023, JTEKT strives to achieve a plastic packaging material basic unit of 0.109 t/100 million yen.
TOPIC
Responding to the Act on Promotion of Resource Circulation for Plastics
In April 2022, the Act on Promotion of Resource Circulation for Plastics came into effect.
In addition to the initiative to reduce single-use plastic consumption that is already being carried out, JTEKT will also promote initiatives to reduce emissions of waste plastics in general.
Activity Details
Reduction of packaging material
Implementation contents
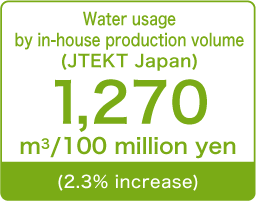
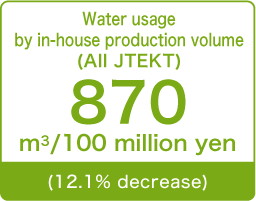
Effective utilization of resources<Reduction of water consumption>
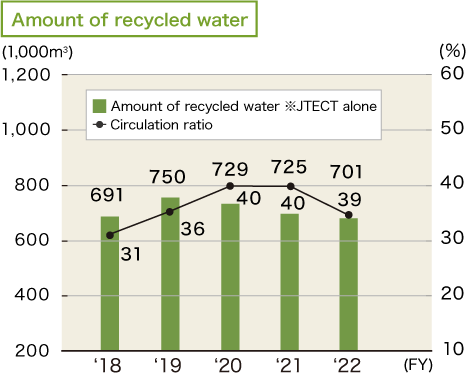
Promoting the effective utilization of water
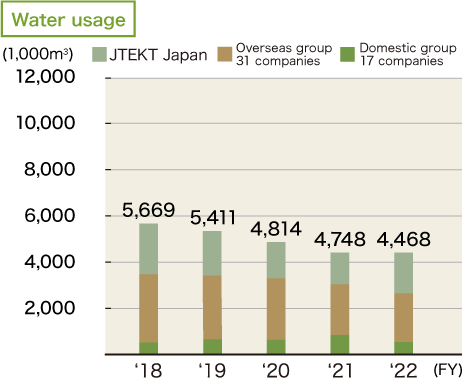
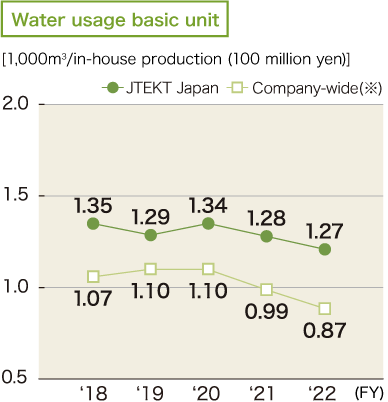
JTEKT is working to control wasteful water use and recycle water within the company in order to reduce consumption of water, which is a precious resource. With the aim of achieving an improvement of 3.0% or more compared to FY2018, in FY2021, JTEKT carried out a reduction in consumption mainly through leakage control. As a result, we were able to achieve our target by taking measures including prevention of unscheduled liquid change. In FY2022, we will further reduce water consumption mainly through leakage control with a target of improvement of 4.0% or more compared to FY2018.
Water risk assessment
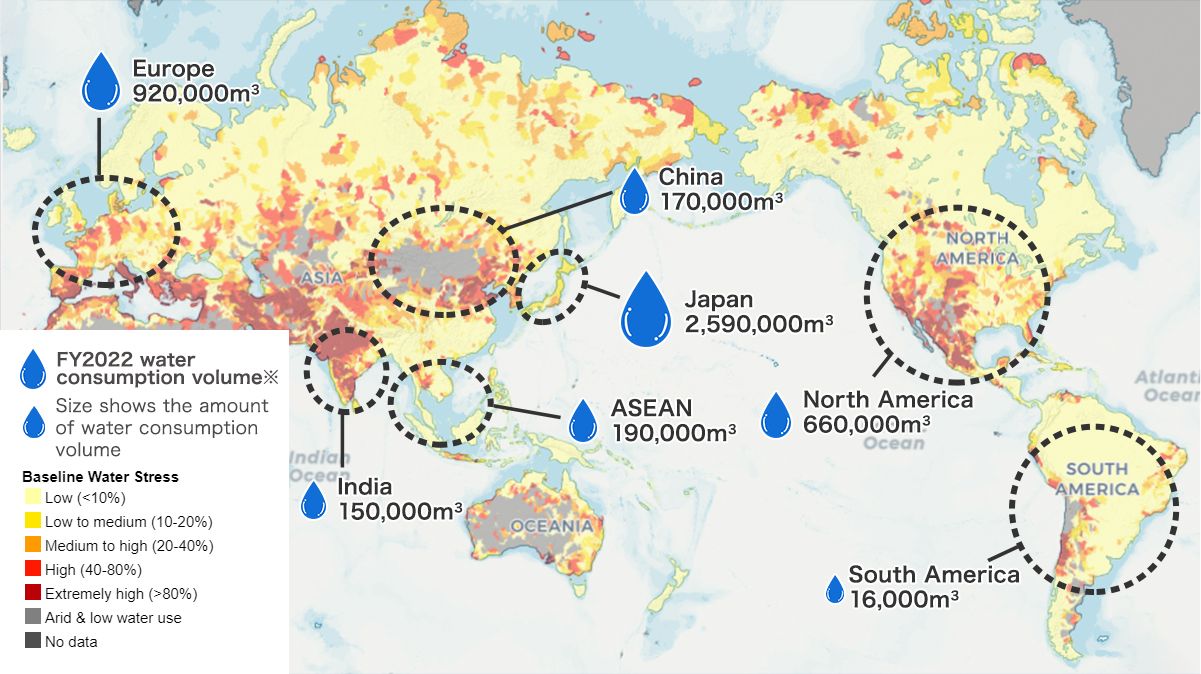
In addition to effectively using water resources by improving the water consumption base unit, JTEKT has been assessing water risks at each business site using Aqueduct* since 2017. JTEKT will continue to work to reduce water consumption and effectively use water resources through activities based on water risk assessment results including future predictions and water consumption and water dependency at each business site.
※Aqueduct
A database operated by the World Resources Institute (WRI) that provides world maps and information showing water risks such as physical water stress, water quality, regulatory risk concerning water resources, and reputational risk.
* Target companies for data collection : Company-wide environmental management companies (JTEKT Japan 13 sites, 17 domestic group companies, 31 overseas group companies)
Water risk countermeasures
JTEKT uses WRI Aqueduct to evaluate water stress, which directly affects our business, to rate high risk business sites as water stressed regions in every fiscal year. We also consider flooding, droughts, regulatory and reputational factors, and future water risk as water stress factors as of 2030. As a result of the FY2022 water risk assessment India and Mexico were rated as the areas having high water stress in all of JTEKT group's production bases.
On top of that, we found from the investigation performed on each region's actual water usage and water situation that the water quality is poor in India. Therefore, water used for production processes at our plants is supplied after improving the water quality by RO (reverse osmosis) membrane equipment installed.
Water stress situation
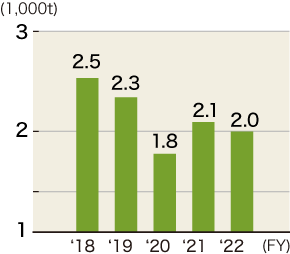
Please refer to the graph below for changes in water usage in water stressed regions. Water usage in stressed regions in FY2022 were 145,000 m3 in India and 10,000 m3 in Mexico. Reduction targets of water usage have been set for each region and measures, such as water recycling and coolant reclamation etc., are being implemented.
India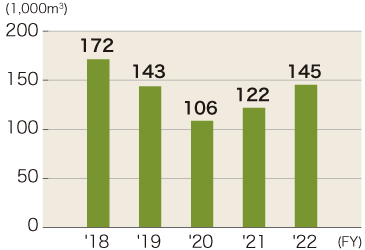
Mexico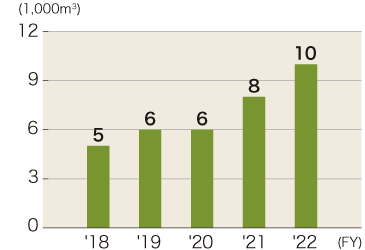
* Newly rated as a water stressed region based on the 2021 WRI Aqueduct assessment
Examples of Water-Saving Initiatives in Water-Risk Areas (India)
Plant : JBIN, JIN
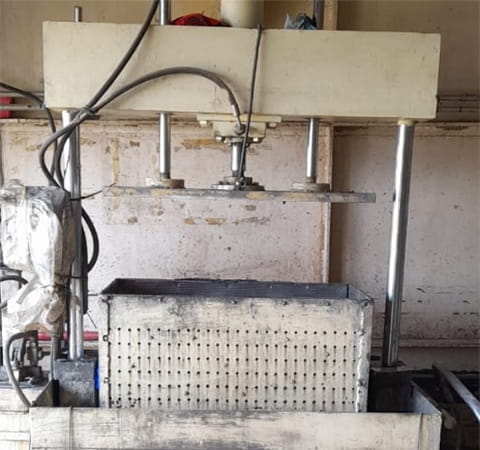

Hydraulic press machine
for separating wet sludge
(JBIN)
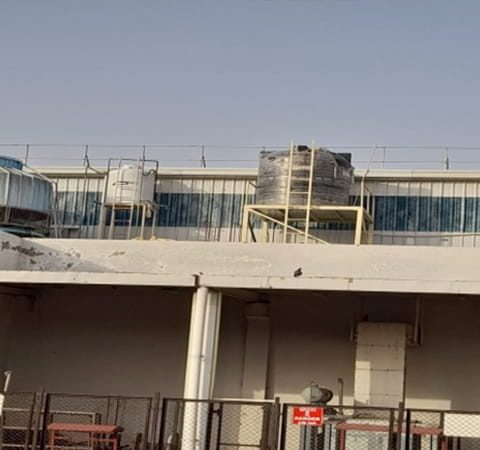

Storage tank for treated water
from sewage treatment plant
(JBIN)

Faucet Shower for
Hand Washing (JIN)
Our SDGs

From left: Subhash, Naveen Kumar, RanVijay, Sanjay Joshi, Sukdeb Sukul
"Achieving water-saving goals by thinking out of the box"
JBIN is working on various improvements to reduce water consumption. Previously, there was no provision to separate wet sludge into coolant and sludge, but we developed a hydraulic press to make this possible, which enables us to re-use approx. 150 liter- coolant per day. We are also working on water-saving by reusing water treated at the sewage treatment plant. Treated water from the sewage treatment plant is stored in an overhead tank and used to flush toilets through pipes, and now, we are saving 3,000 liter-water per day. Since water-saving is the ultimate goal set by JBIN to achieve, our team decided to think out of the box to meet the target. It was a challenging task for the team but we could achieve the target of water-saving.
This is just the start of the water-saving activities, and our team will explore more ideas for the betterment of the society.