What is a Lithium-ion capacitor?
> Inquiries regarding products
What is a Lithium-ion capacitor?
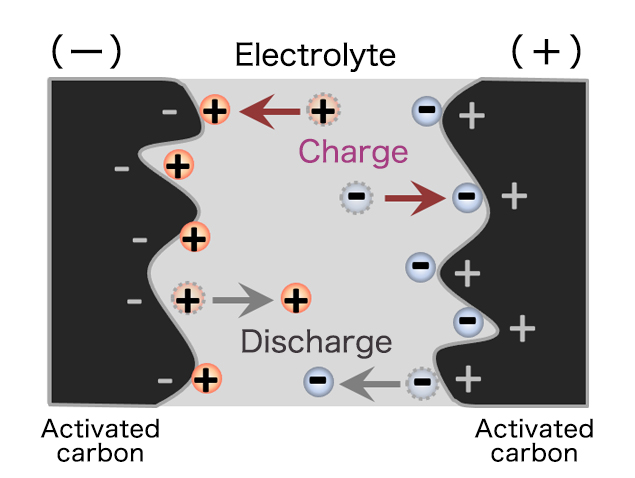
Capacitors are power storage devices that are classified as secondary batteries.Various types of capacitors have been developed depending on the materials used, but there are generally two types of capacitors with large capacities: "Electric Double Layer Capacitors (EDLC)" and "Lithium-ion Capacitors".
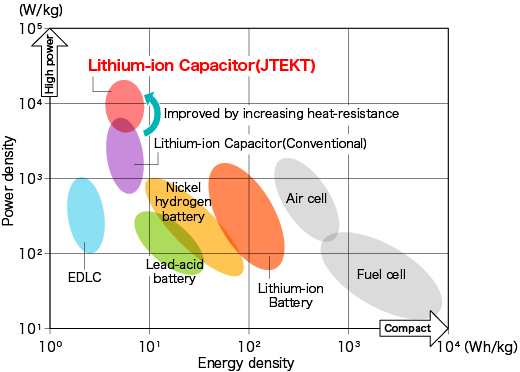
Comparison of power density and energy density for power storage devices
> Click here for glossary about electricity
Features
The feature of capacitors is that electricity goes in and out (charges/discharges) very quickly.Compared to well-known power storage devices (lithium-ion secondary batteries, lead-acid batteries, etc.), the energy density is inferior, but the power density is excellent, the performance deterioration due to repeated charging and discharging is small, and the life is long.
Performance comparison table
◎Excellent、◯Good、△Average
|
|
Libuddy has significantly improved power density and service life due to the wide operating temperature range.
> Click here for glossary about electricity
Principle and structure of Lithium-ion capacitors
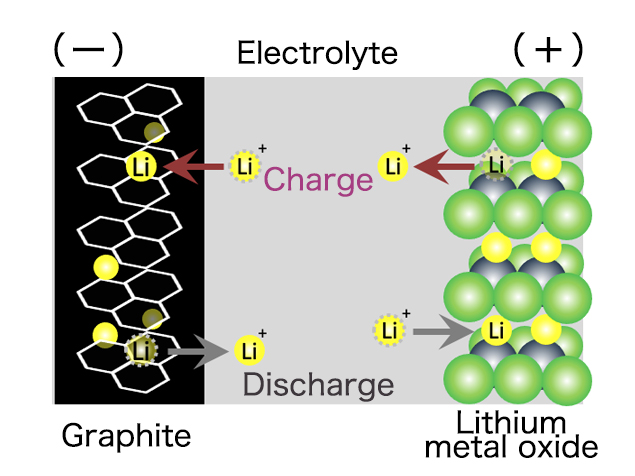
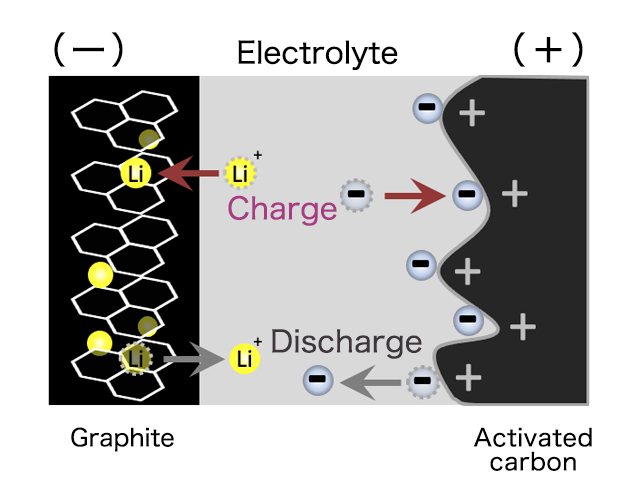
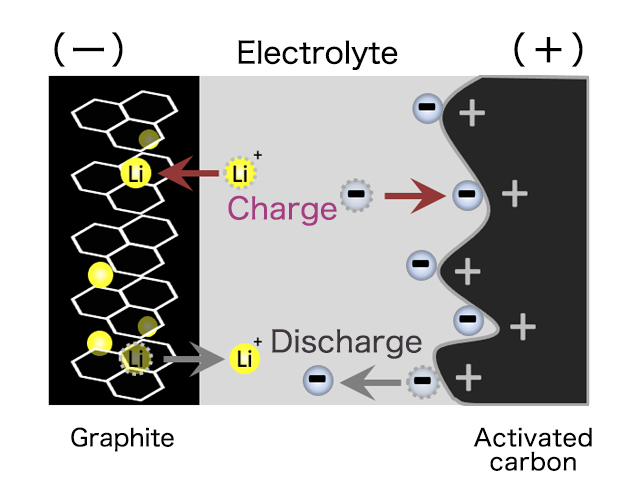
Lithium-ion capacitor combines the positive electrode of EDLC and the negative electrode of a Lithium-ion secondary battery.
This achieves higher energy density than general capacitors and higher safety than general Lithium-ion secondary batteries.
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
There are two types of capacitors, a laminated type and a can type.JTEKT uses the laminated type (shown below).

> Click here for glossary about electricity
Manufacturing method of Lithium-ion capacitor
Lithium-ion capacitors are manufactured in much the same process as Lithium-ion batteries.

General method for manufacturing lithium-ion capacitors
Glossary about electricity
| Current (A) | The number of electrons flowing per second |
|---|---|
| Voltage (V) | The difference in potential between two points |
| Watt (W) | Amount of electrical energy that can be output per second |
| Watt-hour (Wh) | Total electrical energy |
| Internal resistance (mΩ) | Resistance of energy storage devices |
| C-rate (C) | A value that represents the ease of outputting power |
| Joule heat (J) | Heat generated when a current flows through a conductor |
| Primary battery | Batteries that can only be discharged (cannot be charged) |
| Secondary battery | Rechargeable batteries (can be used repeatedly) |
| Float charging | How to charge at a constant voltage |
| Power density (W/L, W/kg) | Power by unit volume or mass |
| Energy density (Wh/L, Wh/kg) | Electric energy by unit volume or mass |
Link
 |
 |