- JTEKT TOP
- Sustainability
- Environmental Report
- Establishment of Low-carbon Society
Establishment of Low-carbon Society
In October 2020, the Japanese government declared its goal to achieve a carbon-neutral, decarbonized society by 2050. Then in 2021, COP26 was held in Glasgow, England, where the goal was formally agreed upon to limit the rise in temperature below 1.5 degrees Celsius versus the temperature level before the industrial revolution, making it a year of accelerated initiatives for the achievement of carbon neutrality.
In order to prevent global warming and mitigate the various impacts of climate change, the JTEKTgroup as a whole will minimize the energy consumption in its business activities, promote energy conservation and logistics improvement throughout all processes from product design to delivery, and promote the use of renewable energy with the aim of achieving carbon neutrality of CO2 in production by 2035.
Major FY2023 Results


Environmental Action Plan 2025 / FY2023 Activity Result
[ ]2013年比
TOPIC
Carbon Pricing Initiative
Carbon pricing is a system that aims to promote a response to climate change by offering economic incentives to reduce CO2 emissions by pricing carbon through carbon taxes and emissions trading.
JTEKT employs an internal carbon pricing system in which an "eco-sheet" stating the energy consumption of the equipment and CO2 emissions per product is attached to approval documents when introducing new equipment. By doing so, we have established investment decision criteria on which we operate to significantly reduce the CO2 basic unit of each newly installed or newly developed product compared to conventional equipment.
Furthermore, to promote investment in emission reduction activities, JTEKT has relaxed the criteria for making investment decisions and expanded the payback period to four years with respect to energy-saving investments in order to encourage active investment and lead to the reduction of CO2 emissions.
Daily improvement initiatives at plant
Reducion of CO2 emissions in production
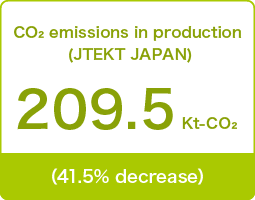
●(JTEKT JAPAN)
JTEKT has set challenge targets to reduce total CO2 emissions by 35% by FY2025 compared with FY2013 and by 60% by FY2030 and is promoting activities.
Total CO2 emissions in FY2023 increased 2% from the previous year to 209.5Kt-CO2 due to the worsening of CO2 conversion factors of electric power companies, but we were able to achieve our FY2023 target with a 41.5% reduction from FY 2013 through energy-saving initiatives and green energy.
In addition, it has been rated as Class A in the FY2023 Business Classification Evaluation System based on the Act on the Rational Use of Energy (hereinafter referred to as the "Energy Conservation Act").
| Total CO2 emissions *1 | 209.5Kt-CO2 (41.5% decrease) |
|---|
*1: Calculated using the actual conversion factor (market basis) for each purchased electric power company for each fiscal year
Total CO2 emissions in production
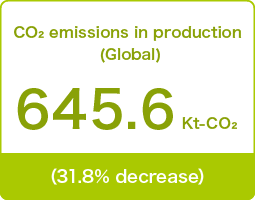
●Global
Total CO2 emissions in FY2023, including domestic and overseas group companies, increased by 4.6% from the previous year to 645.6Kt-CO2 due to the deterioration of the CO2 conversion coefficient, but we were able to achieve the FY2023 target with a 31.7% reduction compared with FY 2013 by improving basic units through energy-saving initiatives. In the future, we will promote activities to achieve the challenge target of reducing energy by 60% by FY2030 through further energy-saving activities and greening energy.
| Total global CO2 emissions | 645.9Kt-CO2 (31.8% decrease) |
|---|
Total Global CO2 Emissions
Initiatives to realize "Environmental Challenge 2050"
JTEKT is promoting various energy-saving measures based on the "Environmental Action Plan 2050" toward the targets set forth in" Environmental Challenge 2050".
Energy-saving diagnosis
In FY 2023, in order to create new energy-saving items and improve the level of energy-saving diagnostic engineers, the in-house diagnosis team conducted diagnoses at the Tokushima Plant and JTEKT METALTEC CORPORATION, a domestic Group company.
Items created through diagnosis are deployed horizontally to all plants, contributing to the promotion of energy-saving activities.
In FY2024, the internal diagnostic team will continue to diagnose internal and domestic Group companies.

Flow measurement of cooling water with ultrasonic flow meter
Improvement example: Toyohashi Plant
Before improvement
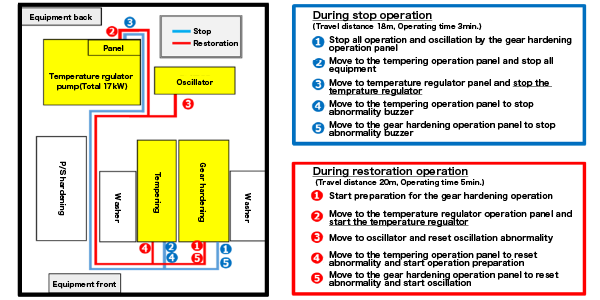
Because the operation switch for the temperature regulator is located behind the equipment, it was necessary to go back and forth several times to stop and restart it, so we could not secure downtime and could not perform non-operating shutdowns such as lunch breaks.
After improvement
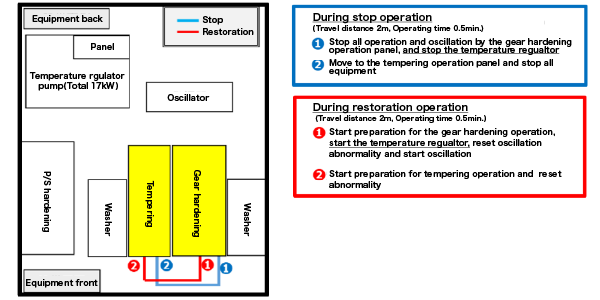
The addition of a temperature regulator operation switch to the production equipment operation panel simplified operations and enabled frequent shutdowns when the machine was not in operation.
[Reduction effects]
・Electricity consumption: Approx. 7,800 kWh/year (approx. 2.9 t-CO2/year)
・Cost: ¥850,000 *Including non-energy costs such as labor costs
Improvement example : Okazaki Plant
Before improvement
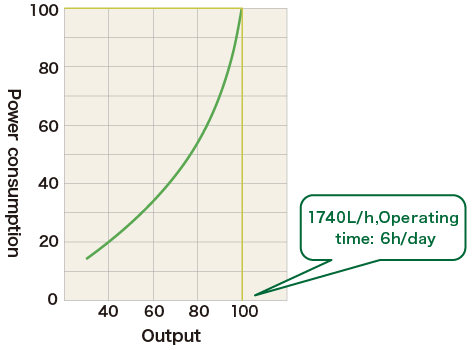
The water supply pump for the exhaust gas boiler of the cogeneration system has a feed rate of 1,740 l/h, which was inefficient operation due to frequent start-and-stop operations when steam consumption was low.
After improvement
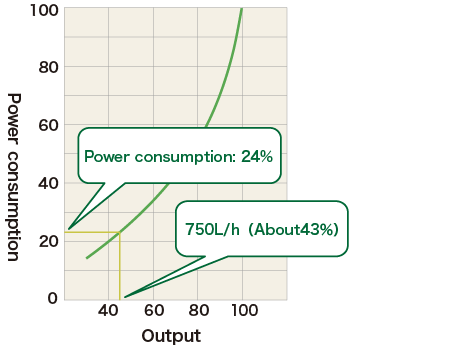
The inverter setting frequency of the feed pump was lowered to 43% and the water supply volume was adjusted to 750 l/h.
Power consumption was reduced by 24% by extending the operating hours from 6h/day to 13.8h/day and reducing the number of starts and stops.
By reducing the number of starts and stops, pump life was also improved from 7years to 10 years.
[Reduction effects]
・Electricity consumption: Approx. 3,500 kWh/year (approx. 1.3 t-CO2/year)
・Cost: ¥80,000 *Including repair cost reduction due to improved pump life
Introduction of renewable energy
In FY2023, a total of 5.04MW of solar power systems were installed at all 9 onsites in Japan and overseas, reducing CO2 emissions by approximately 2,200 tons annually.
As a result, the amount of renewable energy installed became 6.38 MW for JTEKT alone and 37.7MW for the entire JTEKT Group.
With the aim of reducing CO2 emissions, we will continue to actively work to *achieve the challenge target : a renewable energy introduction rate of 60% or more for the entire Group by 2030.
*Renewable energy introduction rate = Amount of renewable power /Total power consumption
Initiatives for the introduction of off-site renewable energy
In FY2023, the JTEKT Group launched its first initiative to procure renewable energy from off-site solar power generation facilities (outside the Company's premises), and signed a virtual Power Purchase Agreement* (PPA) for 142.8 MW in the U.S. and 11.9 MW in Japan.
Under this contract, we will receive the "environmental value" generated by generating renewable energy. This environmental value offsets approximately 124,600 tons of CO2 emissions annually, which is equivalent to the total electricity used by all North American production sites.
The solar power plants to be utilized under this agreement have "additionality", which means that they will be newly installed by the generator. By introducing renewable energy with "additionality," JTEKT will contribute to the expansion of renewable energy throughout society.
* Virtual PPA
A direct power purchase agreement between a power producer and a consumer. Virtual PPA stands for "virtual power purchase agreement," which trades only the environmental value of the power generated from a renewable energy power plant built outside the customer's premises, without electricity based on the amount generated.
Main implementation contents
JTEKT: Tadomisaki Plant
Group companies in Japan: JTEKT GEAR SYSTEMS CORPORATION
Overseas Group Companies: JATH(THAILAND)
In FY2023, JTEKT Tadomisaki Plant introduced a 500kW solar power generation system in the form of a vertically mounted solar power generation equipment (fenced type) that can be installed in a limited space.
Also, JTEKT GEAR SYSTEMS, a Group company in Japan, installed a 1,520kW carport solar power generation system in its employee parking lots.
Since there is a limit to where solar power can be installed at domestic business sites due to the load-bearing capacity of building roofs, we are promoting the introduction of fence-type/carport-type solar power generation systems.
JATH, an overseas group company in Thailand, installed a 968kW solar power generation system. Going forward, we will continue to work on the introduction of renewable energy with low environmental impact and promote the creation of plants in harmony with nature.
JTEKT Tadomisaki Plant

JTEKT GEAR SYSTEMS

JATH (THAILAND)

JATH (THAILAND)
Initiatives to reduce CO2 through production engineering innovation
To achieve carbon neutrality in 2035, we reduced CO2 emissions by 1,353 tons in FY2023 through our production engineering initiatives.
Three major initiatives are being undertaken as carbon neutral activities in production engineering.
① Steady improvement activities
Activities to pursue zero waste in production such as CT shortening, introduction of karakuri (gimmicks), stop in a standby , air minification, downsizing and inverterization
② Production engineering element development
Development of elemental technologies to realize high performance and high efficiency of equipment and construction methods, and machining saving process by considering raw materials, heat treatment, processing, and assembly as a process through.
③ Carbon-neutral innovation development
Development of innovative technologies to replace and recover energy such as gas, electricity and hydrogen with the aim of achieving a revolutionary reduction
Among these initiatives, this time, we will introduce an example of initiatives to achieve carbon neutrality in the heat treatment process of bearings.
Development of one piece-flow IH quenching equipment for deep groove ball bearing
Background and Purpose
The heat treatment process accounts for 22% of total CO2 emissions from all JTEKT processes (Fig. 1). Among them, the production ratio of bearings is high (Fig. 2).
In particular, the larger the outer diameter of the product, the higher the CO2 emission basic unit (Table 1).

Figure 1: Breakdown of CO2 emissions
from JTEKT domestic plants

Figure 2: Comparison of CO2 emissions
by product size

In a geneal heat treatment process for bearings, an atmospheric gas furnace is used, and the energy used to heat and transport the products for heat treatment is only about 20% of the input energy, with the remaining 80% being lost. (Figure 3)
In addition, since the atmosphere gas furnace is a high-volume concentrated process, CO2 emissions from the logistics of the pre- and post-heat treatment processes is one of the issues.
This time, for reducing this energy consumption, we focused on moving away from atmospheric gas furnaces and eliminating logistics between processes, and worked on the development of a heat treatment process for deep groove ball bearings with large product outer diameter.

Figure 3 Breakdown of batch furnace energy consumption
Results of Initiatives
In the conventional manufacturing process for deep groove ball bearings, an atmospheric gas furnace is used for heat treatment heating to quenching (Figure 4),but in the developed process, in order to improve energy efficiency and synchronize the lead time with the pre- and post-process, we adopted induction heating, which enables direct heating of the product and short heating time. (Figure 5)
Moreover, the shape of the quenched coil used for induction heating is optimized by CAE analysis to improve temperature unevenness. (Figure 6)
With these improvements in heating efficiency, the development process has reduced CO2 emissions by ▲45% (Figure 7).
In the future, we will expand to other models to further reduce CO2 emissions.

Figure. 4 General manufacturing process of deep groove ball bearings (excerpt)

Figure 5 Manufacturing process of developed equipment (excerpt)

Figure 6 Optimal design of induction heating coil

Figure 7 CO2 Emissions Reduction Effects
Reduction of CO2 emissions in logistics
In FY2023, we improved our CO2 emissions basic unit by introducing fuel-efficient trucks in cooperation with logistics companies, asking drivers to support eco-driving, and integrating transportation services.In addition, emissions decreased by approximately 25% compared with FY2018 due to improved loading rates and efficiency through the use of Semi-trailer + ship.
In FY2024, we will work to further reduce emissions by optimizing transportation modes (railroads, ships, semi-trailers, etc.), ascertaining changes in cargo volume, and promoting the replacement or elimination of truck services, with a target of 9.1Ktons of emissions.

